Pipes vchshg that. Characteristics of ductile iron pipes, features of production and use. Requirements for ductile pipes
These technical specifications were developed at the Lipetsk Metallurgical Plant "Svobodny Sokol" instead of the technical specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2004 "High-strength cast iron pressure pipes", in connection with the expansion of the range of production of pipes for "TYTON", "RJ", flanged connections.
Technical requirements for pipes, internal cement-sand coating, external anti-corrosion coating, rubber rings are aligned with the recommendations of international ISO standards:
2531, 4179, 8179, 4633; EN 545.
Application area
These technical conditions apply to high-strength cast iron pressure pipes made by centrifugal casting from spheroidal graphite iron (CHG) and intended for water pressure systems, including domestic and drinking water supply.
Pressure pipes are applicable for both channel and channelless underground laying of pipelines. ChShG pipes have a socket part on one side and a smooth end on the other or flanges on both sides for the following types of connections in the pipeline:
- socket connection "TYTON";
- socket connection "RJ";
- flange connection.
These specifications contain requirements for materials, dimensions, tolerances, mechanical properties, test methods for pipes with nominal bore (DN) from 80 to 1000 mm, stoppers and rubber sealing rings. Pressure pipes, for all types of connections, are designed for operation in pipelines with an allowable working pressure specified in Table A.1 (Appendix A).
Nodular cast iron pipelines with an external protective coating can be used in all types of soils. Pipelines and pipes can experience large diametral deflections during operation, while retaining all the functional characteristics, which allows them to withstand a large thickness of the soil cover and heavy road loads. The socket connection ("TYTON" and "RJ") is not rigid and allows the connected pipes to deviate at an angle of 1.5 to 5 °, depending on the diameter of the pipes, while maintaining the complete tightness of the joint.
Permissible deviation angles from the axial line of the pipeline are shown in Figure A.1 and Table A.2 (Appendix A). Connection "TYTON" is a butt socket connection for a sealing rubber ring. During installation, in places of changing the direction of laying the pipeline or reducing the diameter (on tees, turns, transitions), it is necessary to provide stops (reinforcing blocks) to compensate for the forces of axial hydraulic pressure.
Application area
- cold water supply, sewerage.
Connection "RJ" butt socket connection for a sealing rubber ring.
This connection ensures that the pipes cannot be disconnected when laying the pipeline in difficult terrain, in places where there is a danger of soil settlement and under shock loads. The deposited bead on the smooth end of the pipe and the stopper, which are pushed into the recess of the socket after the pipes are joined and fixed with a locking wire, do not allow breaking the connection. This is especially important when installing pipelines in unstable soils, in mountainous areas and in a vertical position of pipes.
Scope - cold water supply, heating systems, sewerage.
The flange connection is rigid and does not allow the connected pipes to deviate from the axial direction.
The design of the flanges varies depending on the working pressure of the pipeline.
Specific equipment is agreed with the manufacturer.
Flanged pipes are predominantly used in surface piping, such as for use in pumping stations, boiler rooms and tanks.
The manufacturer supplies:
Pipes socket class K 9 for connection "TYTON" DN80-DN1000 mm *;
- socket pipes of class K 9 for connection "RJ" DN 80-DN 500 mm? complete with ductile iron stoppers;
- flanged pipes with welded flanges DN 80-DN 1000 mm;
- stopper made of ductile iron for connection "RJ";
- sealing rubber rings for connection "TYTON" and "RJ".
Pipes are supplied:
With external zinc, external varnish and internal cement-sand coating;
- with external varnish and internal cement-sand coating.
When ordering the supply of pipes, it is necessary to indicate the designation index, nominal bore, length, nominal pressure (for flanged pipes), the number of these specifications.
Examples of symbols for pipes, stoppers, sealing rubber rings:
Pipe bell-shaped for connection "TYTON", measured length (6000 mm), DN150 mm: bell-shaped pressure pipe ChShGT-150? 6000.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
Pipe socket for connection "RJ", measured length (6000 mm), DN 200 mm (with stoppers): socket pipe pressure head ChShGR-200? 6000.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
Flanged pipe with welded flanges, fixed length (5500 mm), DN300 mm, nominal pressure 16 bar:
Pipe flange pressure head ChShGF-300? 5500-PN16.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
Sealing rubber ring for connection "TYTON" DN 150 mm: rubber ring T-150.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
Sealing rubber ring for connection "RJ" DN 200 mm: rubber ring R-200.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
Ductile iron stopper for pipes DN 200 mm (left and right): ChShG-200 stopper.
TU 1461-037-50254094-2008.
3 Normative references
This specification uses references to the following standards:
ISO 2531:98 Nodular iron pipes, fittings, fittings and their joints for water and gas supply.
ISO 8179-1 Ductile iron pipes.
Coating with metallic zinc followed by a finishing coat.
ISO 8179-2 Ductile iron pipes.
External coating based on zinc.
Application of zinc enriched paint and finishing coat.
ISO 4179 Ductile iron pipes and fittings for pressure and non-pressure pipelines.
Cement coating.
EN 545:02 Ductile iron pipes, fittings, fittings and fittings for water pipes.
GOST 427-75 Measuring metal rulers.
Specifications.
GOST 3845-75 Metal pipes.
Hydraulic pressure test method.
GOST 1497-84 Metals.
Tensile test methods.
GOST 27208-87 Cast iron castings.
Methods of mechanical tests.
GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire.
GOST 13073-77 Zinc wire.
Specifications.
GOST 7293-85 Cast iron with nodular graphite for castings.
GOST 8736-93 Sand for construction work.
Specifications.
GOST 10178-85 Portland cement and Portland slag cement.
Specifications.
GOST 9012-59 Metals.
Test methods.
Brinell hardness measurement.
GOST 10692-80 Steel pipes, cast iron pipes and fittings for them.
Marking, packaging, transportation, storage.
SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-2001 Hygienic requirements for water quality in centralized drinking water supply systems.
SNiP 2.04.02-84 Water supply.
External networks and structures.
SNiP 3.05.04-85 External networks and facilities for water supply and sewerage.
SNiP III-4-80 Safety in construction.
SNiP 3.01.04-87 Acceptance for operation of completed construction projects.
Basic provisions.
SP 40-109-2006 Design and installation of water and sewer networks using high-strength pipes made of nodular cast iron.
TU 405821-2003 Rubber sealing cuffs for connecting cast iron pipes of the RJ type.
TU 2531-067-50254094-2004 Rubber sealing rings for connecting cast-iron pipes of the TYTON type.
4 Definitions
The following definitions are used in this specification:
4.1 Ductile cast iron with nodular graphite (CHG):
a type of cast iron in which graphite is predominantly present in a nodular form.
4.2 Trumpet:
casting with a uniform channel, with a straight axis, having a smooth, socket or flanged ends.
4.3 Bell:
covering the end of the pipe.
4.4 Smooth finish:
the end of a pipe placed in a socket joint.
4.5 Flange:
flat round end of the pipe, located perpendicular to its axis, with holes for bolts, evenly spaced around the circumference.
4.6 Nominal diameter (DN):
rounded numerical designation of the internal flow area, which is common to all components of the pipeline system.
4.7 Permissible operating pressure:
internal pressure, excluding pressure surges, which the piping components must safely withstand in continuous operation.
4.8 Nominal pressure (PN):
a numerical designation expressed as a number that has reference purposes.
All piping components of the same nominal size, designated by the same pressure rating number, have compatible mating dimensions.
4.9 Pipe class (K):
pipe wall thickness designation coefficient, selected from a number of numbers - 9, 10, 11, 12 ... (an example of calculation is given in Appendix B).
4.10 Party:
the number of castings from which the sample for testing is selected.
5 Technical requirements
5.1 Pipes and stoppers must comply with the requirements of these specifications.
5.2 Pipes and stoppers must be made of cast iron.
5.3 The hardness of the metal should not exceed 230 HB for pipes and 250 HB for stoppers.
5.4 The mechanical properties of the metal of pipes and stoppers, determined when testing specimens for tension, must be at least: tensile strength? c, MPa (kgf / mm 2) 420 (42); conditional yield strength? t, MPa (kgf / mm 2) 300 (30) ?;
relative elongation?, % 10.0.
5.5 Pipes must withstand a test hydraulic pressure of at least: from DN 80 to DN 300 mm5 MPa (50.0 kgf / cm 2); from DN 350 to DN 600 mm4 MPa (40.0 kgf / cm 2); from DN 700 to DN 1000 mm3.2 MPa (32.0 kgf / cm 2).
Each pipe is subjected to leak tests.
5.6 On the outer and inner surfaces of the pipes, defects are allowed that are caused by the method of production and do not affect the tightness of the pipes during a hydraulic test.
5.7 On the inner surface of the socket at the location of the rubber sealing ring, metal and shell flows are not allowed.
5.8 Pipes should not have a straightness deviation of more than 0.125% of their length.
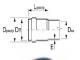
5.9 The dimensions and weight of pipes, flanges, stoppers and sealing rubber rings must correspond to the values indicated in Figures A.2-A.8 and tables A.3-A.9 (Appendix A).
5.10 Socket pipes for “RJ” and “TYTON” connections are supplied with measured length (L) equal to (6000 70 30 +?) mm and (5800 70 30 +?) mm.
Flanged pipes are supplied with L equal to (5500 ±10) mm, or other as agreed with the consumer.
When supplying pipes of one specific length, it is allowed to supply up to 10% of pipes of another specific length with the determination of the total length of the supplied pipes by summing up the effective lengths of the pipes.
5.11 Limit deviations in the pipe wall thickness (S) and in the outer diameter of the cylindrical part (DE) should not exceed the values specified in tables A.3-A.5 (Appendix A).
The plus tolerance for pipe wall thickness is limited by the mass tolerance.
5.12 The deviation of the actual mass of pipes from the theoretical one should not exceed:
± 8% for pipes DN 80 - DN 200 mm inclusive;
± 5% for pipes DN 250 - DN 1000 mm inclusive.
It is allowed to exceed the maximum mass of pipes, provided that all other requirements of these specifications are met.
5.13 For installation and dismantling of pipes for “TYTON” and “RJ” connections, the end of the smooth end of the pipes must have a radius or a chamfer with a transition to a radius according to the dimensions indicated in Figure A.5 and Table A.6 (Appendix A).
5.14 On the outer surface of the smooth end of the pipe under the “RJ” connection, an annular belt is welded according to the dimensions indicated in Figure A.3 and Table A.4 (Appendix A).
5.15 The outer surface of the pipes must be protected with bituminous varnish or other non-toxic material approved by the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare for use as external coatings for pipelines in domestic drinking water supply.
5.15.1 The coating shall comply with the requirements of ISO 8179-2, be homogeneous and cover the entire outer surface of the pipe, and there shall be no unpainted spots or peeling of the coating.
On the surface of the coating, traces of rolling on the elements of equipment are allowed without damaging the paint layer.
5.15.2 The average dry film thickness of the coating should be at least 70 µm, the minimum thickness measured at any point in the pipe should be at least 50 µm.
5.15.3 At the request of the consumer, the outer surface of the pipes can be coated with metallic zinc (zinc content of at least 99%), followed by coating with bituminous varnish.
The zinc coating shall comply with the requirements of ISO 8179-1 and be applied to the entire outer surface of the pipe.
The helical appearance of the coating is acceptable provided that the average weight of zinc should not be less than 130 g/m 2 ?.
5.16 The inner surface of pipe sockets shall be coated with zinc-rich paint (with a zinc content of at least 85%) or metallic zinc, followed by the application of a final layer of bituminous varnish or other non-toxic material.
5.17 The inner surface of the pipes shall be coated with a cement-sand coating in accordance with the requirements of ISO 4179.
5.17.1 The cement-sand pavement shall be continuous and have a smooth surface.
Minor roughness, cracks and sags on the surface of the internal cement-sand coating are allowed, due to the method of applying this coating and not affecting the performance of the pipes.
The width of the opening of longitudinal and transverse shrinkage cracks should be no more than: 0.8 mm for pipes DN 80DN 600 mm;
1.0 mm for pipes DN 700DN 1000 mm.
10 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 Repair of damaged or low-quality sections of the cement-sand coating is allowed.
5.17.2 The thickness of the cement-sand coating applied to the inner surface of the pipes must correspond to the following characteristics: the optimal coating thickness (S 1) must correspond to the values \u200b\u200bspecified in tables A.3, A.4 (Appendix A); the average value of the coating thickness should be not less than 2.5 mm;
the minimum thickness measured at any point in the pipe must be at least 1.5 mm.
It is allowed to reduce the thickness of the cement-sand coating less than 1.5 mm at a distance of not more than 50 mm from the ends of the pipe.
5.17.3 It is allowed to apply other material on the inner surface of the pipes, permitted by the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare, for use in domestic drinking water supply.
It is allowed to use materials that have a hygienic certificate or a certificate of conformity with a reference to the hygienic certificate for the intended use of the material.
5.18 Flanged pipes are supplied uncoated.
At the request of the consumer, flanged pipes are supplied with external and internal coating.
5.19 Permissible deviations for machining and drilling of flanges are set as follows: according to the diameter of the bolt holes in the flanges + 1.0 mm;
by the distance between the centers of the holes ± 0.5 mm;
on the thickness of the machined flange ± 1.0 mm;
displacement of the center of the circle of the location of the centers of the bolt holes relative to the center of the inner diameter of the flange ± 1 mm.
5.20 Completeness.
5.20.1 Pipes for TYTON and RJ connections are supplied to the consumer complete with sealing rubber rings.
The composition of the material and properties of sealing rubber rings are regulated by the specifications of the ring manufacturer (TU 2531-067-50254094-2004, TU 405821-2003).
5.20.2 Pipes for “RJ” connection are supplied to the consumer complete with stoppers.
The dimensions and weight of the stoppers shall be in accordance with Figure A.6 and Table A.7 (Appendix A).
Low-carbon steel wire according to GOST 3282 is welded into the left stopper.
5.20.3 At the request of the consumer, pipes can be supplied complete with a polyethylene film (sleeve) designed to provide additional protection of pipelines from corrosion.
The sleeve is put on pipes directly before their laying.
The dimensions of the polyethylene sleeve shall be in accordance with Figure A.9 and Table A.10 (Appendix A).
5.21 Pipes must have a cast marking in the socket, on which the following designations must be applied Specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2008 JSC LMZ Svobodny Sokol
11 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 trademark of the manufacturer;
conditional pass;
Year of manufacture;
designation that the material is spheroidal graphite cast iron (ChShG, VCh or GGG).
5.22 Pipe packaging and additional marking in accordance with GOST 10692.
6 Safety and environmental requirements
6.1 Pipes are explosion-proof, non-toxic, electrically safe and radiation-safe.
Special security measures are not required during the entire service life of the pipes.
6.2 The safety of pipes during operation is ensured by: mechanical and technological properties of pipes;
high cold resistance and corrosion resistance of metal;
carrying out hydraulic tests;
using protective coatings.
6.3 During testing, storage, transportation and operation, pipes are environmentally friendly products.
6.4 Pipe production waste should be used for recycling.
7 Acceptance rules
7.1 Pipes and stoppers are presented for acceptance in batches.
The number of castings to be checked in a batch is set by the manufacturer.
7.2 Pipes made of ductile iron are subjected to the following types of control: visual control;
measuring control;
hydraulic test;
unbrakable control;
hardness control;
control of mechanical properties.
7.3 Hydraulic test, visual, measurement and non-destructive testing must be carried out for each pipe.
7.4 Checking the hardness and mechanical properties of the metal is carried out on samples made from any pipe in the tested batch.
7.5 Checking the mechanical properties of cast iron stoppers is carried out on one product from a batch or a separately cast sample.
7.6 Upon receipt of unsatisfactory test results for at least one of the indicators, repeated tests are carried out for this indicator of a double number of samples taken from the same batch.
The retest results apply to the entire lot.
Specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2008 OJSC LMZ Svobodny Sokol High-strength cast iron pressure pipes Edition No. 3 p.
12 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 It is allowed, in case of unsatisfactory results of repeated tests, to subject each product to piece-by-piece control for an unfulfilled indicator.
7.7 The results of a hydraulic test of pipes are considered satisfactory if no visible leakage, sweating or other sign of damage is found on their outer surface.
7.8 The thickness of the external bituminous and internal cement-sand coating is checked on at least one pipe of each diameter from the batch.
7.9 Control of zinc coating weight is checked during pipe production at least once a month according to the manufacturer's method.
8 Test methods
8.1 To carry out mechanical tests and determine the hardness of pipe metal, a ring is cut from the smooth end of the selected pipe, from which three samples are made.
Samples are manufactured and tested in accordance with GOST 1497 and GOST 27208, E H 545.
8.2 To carry out mechanical tests and determine the hardness of the stopper metal, separately cast blanks are used in accordance with GOST 7293 or samples made from parts.
8.3 The hardness test of the metal of pipes and stoppers is carried out in accordance with GOST 9012.
8.4 Hydraulic testing of pipes is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845.
8.5 Non-destructive testing is carried out according to the manufacturer's method.
8.6 Inspection of pipes is carried out visually, without the use of magnifying devices.
8.7 The geometric dimensions of pipes and stoppers are controlled by standard measuring tools according to GOST 427 or a tool made according to the manufacturer's drawings.
8.8 Checking the straightness of pipes is carried out visually.
In case of doubt, the deflection may be measured with a ruler and feeler gauges or by other means according to the manufacturer's procedure.
8.9 The composition and properties of the cement-sand coating are regulated by the technical documentation of the manufacturer and GOST 10188, GOST 8736.
8.9.1 The quality control of the cement-sand coating applied to the pipe is carried out visually and using instrumental methods of control.
8.9.2 The thickness of the internal cement-sand coating of pipes is controlled immediately after its application by piercing with a special probe made according to the manufacturer's drawings.
8.9.3 The average value of the thickness of the internal cement-sand coating is measured in any section perpendicular to the axis of the pipe at 4 points, separated by intervals of 90 0, at a distance of at least 200 mm from the smooth end.
Specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2008 OJSC LMZ Svobodny Sokol High-strength cast iron pressure pipes Edition No. 3 p.
13 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 8.10 The quality control of the external bituminous coating is carried out visually.
8.10.1 The thickness of the bituminous coating is measured according to the manufacturer's method.
8.11 Weight control of zinc coating is carried out according to the method described in ISO 8179-1.
9 Transport and storage
9.1 Transportation and storage of pipes must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of GOST 10692 and SP 40-109-2006.
9.2 Pipes DN 80 - DN 300 are transported in bags?.
The number of pipes in packages is regulated by the manufacturer's documentation.
Pipes DN 350 - DN 1000 are transported without packages.
Plastic plugs are installed on the smooth ends and sockets of pipes DN80 - DN 500.
9.3 Vehicles must be suitable for transporting, loading and unloading pipes.
To reduce the risk of accidents during transportation, the following rules must be observed: do not allow direct contact of the pipes with the bottom of the vehicle (place the pipes horizontally, on two parallel wooden beams); during transportation, use side supports (stops) in order to stabilize the load;
secure the load with textile belts and tensioning devices;
during transportation, check that the cargo is in a fixed state;
when transporting pipes by road, the length of the hanging ends should not exceed 25% of the length of the pipe;
do not allow the pipes to come into contact with the metal surfaces of the vehicle in order to avoid damage to the outer coating.
Subject to the above rules, ductile iron pipes may be transported by any means of transport.
9.4 Storage of pipes in warehouses and construction sites is carried out in transport packages or without packages in specially equipped stacks.
9.4.1 Packages of pipes can be stacked on bars of 80? 80? 2600 mm, 3 or 4 bags in each row.
Each subsequent tier of packages is separated from the previous one by bars, the thickness of which is slightly greater than the numerical value of the difference between the diameters of the socket and the pipe cylinder (s > D - DE).
The total height of the stack should not exceed 2.5 m.
Periodically it is necessary to check the condition of the packages, as well as the overall stability of the stack.
By agreement with the consumer, pipes DN 80-DN 300 can be transported without packages.
Specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2008 OJSC LMZ Svobodny Sokol High-strength cast iron pressure pipes Edition No. 3 p.
14 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 9.4.2 Stacking of non-bundled pipes must be carried out on even solid foundations.
Rows of stacked pipes should be laid on wooden spacers.
In this case, it is necessary to provide side supports that prevent spontaneous rolling of pipes.
9.5 Stoppers for connection "RJ" are stored in open containers, sorted by diameters.
9.6 Rings are transported by any transport in compliance with the transportation rules established for this type of transport.
Sealing rubber rings should be stored in accordance with the recommendations of ISO 2230 indoors at temperatures from 0 to +25 0 С at a distance of at least 1 m from heating devices and be protected from direct sunlight and artificial lighting with high ultraviolet radiation.
It is not allowed to pollute with substances that have a harmful effect on rubber (oils, kerosene, gasoline, acids, alkalis, etc.).
The seals must not be stored in a room with any equipment capable of generating ozone, such as mercury vapor lamps or high voltage electrical equipment that may produce electrical flashes or silent electrical discharges.
Seals must be stored free of stress, compression or other deformation.
Seals must be kept clean.
As an exception, it is allowed to store rings in unheated warehouses at a temperature not lower than minus 25 ° C, but it is forbidden to subject them to any deformation and shock loads.
Rings after transportation or storage at temperatures below 0 ° C, before installation, must be kept at a temperature of (20 ± 5) ° C for 24 hours.
9.7 For each batch of pipes shipped to the consumer, the Supplier issues a document on the quality of pipes, which must indicate:
name of the manufacturer, nominal diameter of pipes, their number and total length in meters, theoretical weight, type and number of sealing rings, hydraulic test pressure, tensile strength, relative elongation and hardness of pipe metal.
10 Guidelines for the operation of pipelines
10.1 When designing, performing and accepting work on the construction, reconstruction and repair of pipelines, the requirements of SP 40-109-2006, SNiP 2.04.02, SNiP 3.05.04, SNiP III-4 and other chapters of SNiP for the organization of construction, relevant state standards and norms Specifications TU 1461-037-50254094-2008 OJSC LMZ Svobodny Sokol High-strength cast-iron pressure pipes Edition No. 3 p.
15 of 28 OKP 146100 Group B 61 mother documents on environmental and fire safety in the course of work.
10.2 Installation of pipelines must be carried out taking into account the requirements of SNiP 3.05.04, SP 40-109-2006.
10.3 Testing of water supply networks should be carried out taking into account the basic requirements of SP 40-109-2006, SNiP 2.04.02, SNiP 3.05.04 and in accordance with the project.
10.4 The procedure for flushing and disinfection of pipelines is adopted in accordance with SNiP 3.05.04 and SanPiN 2.1.4.1074. 

Annex B
(informational)
Classes K for pipes and fittings (Extract from EN 545)
The nominal wall thickness of cast iron pipes and fittings is calculated as a function of the nominal diameter DN according to the following formula, with a minimum value for pipes of 6 mm and for fittings of 7 mm:
e \u003d K (0.5 + 0.001DN),
where e is the nominal wall thickness in mm;
DN - conditional passage;
K is a factor used to designate the wall thickness class.
Usually integer numbers are chosen for designation: ... 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ...
 >
>
When a water pipe is being installed, the attention of engineers and builders is riveted to the laying technology and the choice of materials. A worthy alternative to products is a ductile iron pipe. Its base is cast iron. The material does not at all limit the scope of such pipes only for sewage. On the contrary, some features of the production process make it possible to create a product that is in demand in the construction of residential, public and highly specialized facilities.
The device of the pipe speaks of its solid structureWhat is the abbreviation hiding?
Deciphering ductile iron will give a description of the material from which it is produced with nodular graphite. Unlike steel communications, such pipelines are not afraid of corrosion, are cheaper and easy to install. open the list of positive qualities that ductile iron pipes possess. By what means is this achieved?
The secret of combining carbon and iron, or how iron and steel are born from manufacturers: the price is responsible for the quality
Metallurgy is not limited to the production of steel and iron, but these products have found distribution in everyday life. Both alloys require two main components: iron and carbon. Their compounds with the addition of alloying components give one or another material at the output.
Scheme 1. Composite components of iron and steelGraphite is one of the states of carbon. When it is combined with iron in the right state, a strong and hard material is obtained. Gray cast iron, in which the carbon particles take on a flat shape, is soft and ductile. In the process of crystallization, nodular graphite is formed, with which cast iron becomes high-strength.
Characteristics of ductile iron pipes in a case: weight, dimensions, etc.
- outdoor heating networks, where the water t reaches 150 ° C;
- pipelines for the chemical and oil refining industries;
- water supply networks;
- non-pressure and pressure sewerage;
- fire pipelines.
This list is not final and is constantly updated.
Production standards in accordance with GOST with a certificate: diameters 100, 200, 150, 300, 400
Their most practical ductile iron products. In order for them to meet the tasks set, there is a standard for their production. GOST is a system of norms, rules and characteristics for various products. A regulatory document was also developed for cast iron pipes. It is important to understand that in each of the industries there are certain requirements.
So the dimensions of ductile iron pipes correspond to GOST 9583-75. He divides products into 3 types: A, B and LA. A manufacturer who wants to comply with the standards faces a difficulty: GOST is designed for casting products from cast iron of a different brand (graphite inclusions in it are in the form of plates). Of the regulatory documents related to the design and installation of communications from ductile iron pipes, one can name TU 14-161-183-2000 and SP 40-106-202.
Another GOST of ductile iron pipes is 7293-85, it regulates the grades of cast iron for castings based on their mechanical properties.
In our country, ductile iron products are produced by Lipetsk Svobodny Sokol. Casting of products is carried out according to TU 1461-037-50254094-2008. Cast iron pipes VChShG Svobodny Falcon differ insignificantly from GOST in size: the range of sizes is 80 - 1000 mm.
Svobodny Sokol company specializes in the production of such pipesProducts of different classes with the same outer diameter will differ in wall thickness and weight.
When purchasing products from ductile iron, it should be borne in mind that manufacturers work according to specifications and carefully study the attached documentation on the assortment.
Despite the confusion in the documents, Svobodny Sokol ductile iron pipes are in demand.
Description and purpose of external and internal coating: connection of cast-iron pipes with CPP (cement-sand coating)
Ductile iron products are sometimes referred to as: VSHCHG 300 pipe with CPP. The numbers indicate the size, and the abbreviation stands for cement-sand coating. It is applied for additional protection against corrosion and improves the hydraulic characteristics of products. The thickness of the layer, its composition and method of application are different, but it always helps to keep the water flow coefficient in. The ductile iron pipe is a guarantor of the strength of communications.
Outside, a zinc layer coated with bituminous varnish is applied. With such processing, the pipeline is able to function even in difficult conditions. The scope of ductile iron pipes is quite large.
Black bituminous lacquer is coated on top of the pipe - this is a feature of the productionReasons for the popularity of installing Rj socket pipes for sewerage: why do we need fittings
The advantages of ductile iron pipes are obvious:
- service life 80 - 100 years;
- ease of connection ensures quick installation of the entire system;
- cold resistance up to - 60 ° C;
- transported water retains its quality;
- resistance to corrosion;
- plasticity, resistance to damage.
Comparative analysis and studies have confirmed that communications laid using ductile iron pipes are characterized by the least accident rate. They are laid to a depth of 8 to 10 m, laid in an arc with a large bending radius, without using fittings.
The price of ductile iron pipes is able to compete with similar products made from other materials.
Table 1. Approximate cost of products
WATCH VIDEO
Thus, the technical features of ductile iron pipes are successfully combined with the economic efficiency of the communications being created. The maintenance of such pipelines is considered low-cost, and at the end of their service life, all elements can be disposed of. The ductile iron pipe is very popular in the industry.
VChShG is high-strength cast iron with nodular graphite. It was created in the middle of the last century by American scientists. VChShG serves as a raw material for the manufacture of pipe products. Not only abroad, but also in Russia, ductile iron pipes have long been produced, which are used in various industries.
VChSHG pipe its features and scope
VChShG pipes differ:
- strength;
- plasticity;
- resistance to aggressive environment;
- long service life and easy maintenance.
Ductile iron pipes are most often produced under the cuff, which reduces installation time and simplifies it.
 Ductile iron pipes will be the best choice for the installation of underground water pipes and waste disposal; such a sewer will last more than 100 years. For the transportation of drinking water, cast iron products with nodular graphite with a CPP, that is, with a cement-sand coating, are used.
Ductile iron pipes will be the best choice for the installation of underground water pipes and waste disposal; such a sewer will last more than 100 years. For the transportation of drinking water, cast iron products with nodular graphite with a CPP, that is, with a cement-sand coating, are used.
Loyal prices for cast-iron pipes for clients of TSK Industry + LLC
The price of ductile iron products on the website of TSK Industry + LLC corresponds to its high quality and allows you to profitably purchase any number of meters of pipes.
Large selection of ductile iron pipes on our website
For customers who value their own time, we offer to place an express order on the website. You can learn more about ductile iron pipes and their characteristics during a conversation with our managers.
Most often, pipes made of cast iron - an iron alloy with a high carbon content - are used in sewer systems. But, in addition to this area, ductile iron pipes have also found application in the construction of heating mains, water pipelines and gas mains, as well as in the oil sector, when creating wells. This article is about the properties of VSHCHG, areas of application and installation of products from this material.
What is VCHSHG?
First of all, it should be noted that for the term ductile iron pipe, the interpretation is quite simple: it is a pipe made of ductile iron with nodular graphite.
As you know, cast iron contains a large amount of carbon. By processing the alloy in a steel-smelting apparatus with forced access of air, which saturates the melt with oxygen, steel is obtained in which there is much less carbon. Excess carbon goes into the carbon dioxide formed during the melting process.
Steel has the following advantages over cast iron:
- high resistance to sharp (shock) loads;
- the best indicators of plasticity and viscosity, providing additional strength of the material.

The main disadvantage of steel is its tendency to corrosion, which makes it difficult to use the alloy in sewer systems. To solve this problem, it is possible to create a protective coating (zinc, chromium, etc.) on the surface of steel pipes or to produce steel of special stainless grades (with the addition of vanadium, titanium, chromium and other substances), however, in both cases, the price products are markedly increased.
A way out of the situation was found in 1943, when during the regular convention of the American Foundry Association, the idea was introduced that the form of graphite contained in cast iron could be modified in order to control its properties. As a result, after a very short time, the scientist K. Millis succeeded in replacing the previously existing lamellar form of graphite with a spherical one in gray cast iron.

This was achieved by introducing a small amount of magnesium into the melt. As a result, a very corrosion-resistant, inexpensive material became available to the end customer, in Russian and denoted by the abbreviation VChShG.
Characteristics and applications of the material
The properties of ductile iron pipes in Russia are regulated by GOST 7293-85.
Advantages of VChSHG:
- excellent casting qualities;
- high strength, guaranteeing a long service life of products;
- good ductility combined with toughness;
- resistance to points of emerging concentrated stress;
- the ability to tolerate cyclic loads well;
- the possibility of processing products by cutting;
- material safety, environmental friendliness and the possibility of complete processing of products that have become unusable;
- resistance to high pressure and temperature;
- maintaining performance in case of changes in external temperature and humidity;
- the ability to transport chemically aggressive media.

The material having such technological parameters can be used:
- As an alternative to gray cast iron - with an increase in service life and other important indicators.
- As a replacement for steel - in addition to reducing the cost of production, the advantages of this technological solution are the reduction in alloy consumption and the simplification of the casting process.
- Instead of alloys based on various non-ferrous metals - as in the second case, the main benefit of the replacement is a reduction in the price of the material.
Methods for the production of pipes from ductile iron
Since high-strength cast iron with spherical graphite is very much in demand in the industry, its production is gaining momentum every year, therefore, the number of methods for obtaining this inexpensive high-quality material is also increasing.
Today, along with the traditional additive - magnesium - substances such as calcium, rare earth metals and others are actively used.

Yet the most popular, partly due to familiarity, is the process using magnesium or magnesium-containing additives (ligatures).
The dimensions of ductile iron pipes obtained at the outlet do not affect the method of their manufacture. Today, casting of such products is the cheapest and technologically preferable.
Requirements for ductile iron pipes
The system of requirements for such pipes is rather confusing, regulated both by GOST and other regulatory documents.
For example, when constructing underground pipelines from ductile iron, the assembly features of these circuits are determined by SP 40-106-202.
Standard characteristics and methods of using pressure pipes made of the same material are regulated by TU 14-161-183-2000.

However, in both cases, the range of products is regulated by GOST 9583-75, according to which three classes of pipes are distinguished by wall thickness: LA, A, B. For each wall thickness, its own system of standard sizes is provided, including such parameters as nominal bore, outer diameter of the product , weight of the pipe depending on the length (values are provided in the range of 2-10 m in increments of 1 m) and the weight of a running meter of the product.
Enterprises have the opportunity to manufacture products according to specifications. For example, the Svobodny Sokol plant produces ductile iron pipes not only with sockets, but also with the possibility of flange connection. It is worth noting that socketless cast-iron sewers are becoming more and more popular.
For transmission through the water supply system, ductile iron pipes with a CPP (cement-sand coating) are produced from this material of drinking water, which excludes the formation of slag in the pipe and enhances the protection of the inner surface of the product from corrosion. As a result, the quality of the supplied water complies with SanPiN.

CPP provides the pipe with both passive protection (as a coating on the surface of the product) and active (during wetting, calcium hydroxide is formed in the micropores of the pipe, which passivates iron with the formation of a surface film and thus protects it from destruction due to corrosion).
Features of connecting products
Installation of ductile iron pipes is carried out in two ways: by electric welding and by connection into a socket.
The first option is carried out using special electrodes.

The algorithm for creating a socket connection:
- Clean the inner surface of the socket, removing dirt, grease, sand particles, etc. Do the same with the end of the second pipe, checking for the presence of a chamfer and, if necessary, cutting it yourself. Lubricate the end with a special paste.
- After checking the integrity of the cuff, fold it in the shape of a heart and put it into the socket with a little effort. Apply the paste to the open area of the product.
- Align the end of the second pipe with a mark in the socket applied at a distance of the depth of the socket minus 1 cm, fix it with improvised means and compress the connection.
In the case of conscientious execution of the connection, the assembled circuit will last a long time without requiring urgent repairs.
The Pipe Solution company offers to order ductile iron pipes of excellent quality and at an affordable price. We sell products throughout the Russian Federation and CIS countries. A large list of various logistics companies and many years of experience of our specialists in the field of cargo delivery will allow you to choose the most optimal option that matches the urgency of delivery and your region. You can contact our staff by email: [email protected].
Description of ductile iron pipes GOST
Ductile iron pipes interspersed with graphite have a whole list of positive characteristics. Mainly, this is a high anti-corrosion resistance of the material and mechanical resistance parameters - metal ductility, strength characteristics to impact and tear, and others. These indicators are achieved by modifying the cast iron material with magnesium. In the structure of cast iron, spherical graphite particles are formed, which prevent any cracking of the material, while giving it ductility and additional strength.

The use of these products is common in many household and industrial areas. These pipes are widely used for sewerage, in water supply systems - when transporting liquids and gas, in systems used under pressure and without it, in ground and underground communications, drains and many other needs.
ductile iron pipes price which, distinguished by its availability and profitability of investments, exceeds steel products in terms of durability by 5 times. Periods of trouble-free operation reach 100 years. Such products are used directly in soil rocks. Cast iron perfectly tolerates shock, pressure and temperature drops, which allows it to be used in the most aggressive climates. He is not afraid of cold, earthquakes and subsidence of the soil.
The impact-viscosity characteristics of such products do not change in the range from 0 to -60 degrees Celsius.
Ductile iron pipes have a non-rigid socket connection and make it possible to maintain the tightness of joints for pipe products with remote control from 100 up to 150 millimeters and at an angle of up to 50 degrees, as well as for pipes with remote control from 200 before 300 millimeters and an angle of up to 40 gr.
Issues of purchasing ductile iron pipes
The pricing policy for these products depends on the type of processing used, the use of the packaged part and other conditions. Such products are often additionally galvanized or clad with bituminous varnish, which has a positive effect on the operational life of the pipe, adding additional time to an already long period of use. Indicators of diameter and length - make their own adjustments to the cost of production. To clarify the cost and order details, you can contact the managers of the Pipe Solution company at the number indicated on the official website: 8-800-500-69-53. Our experts will advise you on the availability of goods in stock, as well as help with the selection and the necessary characteristics of pipes for your application.